Recognizing One Million Celebrities
Task Description
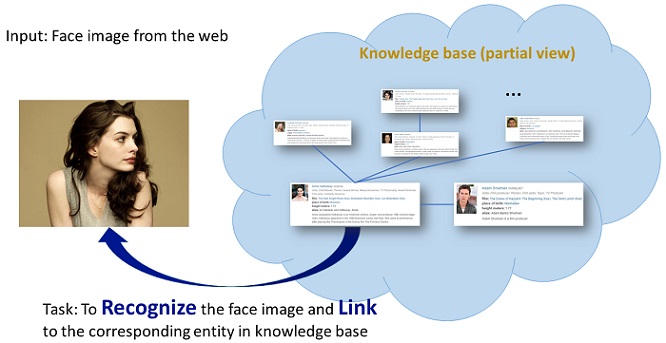
The challenge is to recognize one million celebrities from their face images and identify them by linking to the unique entity keys in a knowledge base. This task introduces very large scale face recognition with disambiguation. More specifically, our task has the following properties.
-
We introduce a knowledge base (Freebase) into face recognition, since the recent advance in knowledge bases has demonstrated incredible capability of providing accurate identifiers and rich properties for celebrities.
-
Recognizing celebrities, rather than a pre-selected private group of people, represents public interest and could be directly applied to a wide range of real scenarios Moreover, only with popular celebrities, we can leverage the existing information (e.g. name, profession) in the knowledge base and the information on the web to build a large-scale dataset which is publicly available for training, measurement, and re-distributing under certain licenses.
-
We select one million celebrities from Freebase according to their occurrence frequencies (popularities) on the web. Considering each entity as one class may lead to, to the best of our knowledge, the largest classification problem in computer vision. The clear definition and mutually exclusiveness of these classes are supported by the unique entity keys and their associated properties provided by the knowledge base.
We provide training and measurement set for the given challenge, with descriptions here. Participants are encouraged to build recognition system based on, but not limited to, our training data.
Evaluation
Our measurement set consists of images for a subset of celebrities in our one-million celebrity list. Currently, we select 1000 celebrities and carefully label about 30 images per celebrity. We select two images per celebrity from all the labeled images and form the following two sets.
-
Random set: The image in this subset is randomly selected from the labeled images. One image per celebrity. This set reveals how many celebrities are truly covered by the models to be tested.
-
Hard set: The image in this subset is the one (from the labeled images) which is the most different from any images in the training dataset. One image per celebrity. This set is to evaluate the generalization ability of the model, and the robustness of the model on complex situations caused by pose/age/resolution/special effects/etc..
In order to make our measurement more challenging, we blend a set of distractor images with both these sets of carefully labeled images. The distractor images are images of other celebrities or ordinary people on the web, which are mainly used to hide the celebrities we select in the measurement.
We evaluate the recognition system with both the sets and rank the results seperately. A contesting system is asked to produce at least one prediction label with a confidence score per test image (including both labeled image and distractors). To match with real scenarios, we measure the recognition recall at a given precision 95% for both the sets. That is, for N images in the measurement set, if an algorithm recognizes M images, among which C images are correct, we will calculate precision and recall as:
precision = C/M
coverage = M/N
By varying the recognition confidence threshold, we can determine the coverage when the precision is at 95%. Note that we ignore distractor images in this evaluation metric.
Note: Commercial/public intelligent services are not allowed to be called during the evaluation, e.g. Microsoft Cognitive Servcies, etc. We will detect and ban the contestants for this kind of behavior.